Looking for a collection of no-nonsense SEO tips, that you can easily implement to boost your site’s search engine rankings?
Then look no further.
We’ve created a list of over 100 SEO tips and best pratices and split them into logical sections to cover various aspects of search engine optimisation – from on-page factors, to user experience, link building and more.
For most tips you will also find a link to further reading; including official Google guidelines where relevant and a hand picked selection of some of the very best SEO guides on the web.
To jump to a specific section, use the quick links on the right, otherwise, let’s get started!
Part 1: Site Layout & Architecture
1. Ensure content is clear and upfront – Content should be front and centre on any web page. At a minimum the page’s title should be ‘above the fold’; that is visible without the visitor having to scroll. (further reading)
2. Avoid too many ads above the fold – While display advertising is an essential revenue model for many websites, too many ads above the fold may impact negatively on search rankings. Ensure any display advertising is non intrusive and clearly distinguishable from content. (further reading)
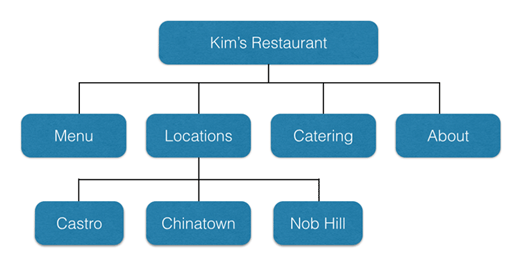
3. Create a content hierarchy – A well designed hierarchy keeps content organised and allows pagerank to flow effectively round a website, boosting key ‘hub’ pages.
4. Ensure navigation is clear – Navigation should be easy to locate and intuitive for both search engines and users. (further reading)
5. Nofollow any paid/affiliate links – All paid links should have the rel=”nofollow” attribute added. This includes affiliate links. (further reading)
<a href="http://www.example.com" rel="nofollow">Paid Link</a>
6. Use SEO friendly URLs – URLs should be human readable and follow a logical structure. Short URLs which include target keywords (separated by hyphens) are considered best for SEO. (further reading)
7. Ensure you have clearly visible contact information – Contact details should be easy to find and ideally should include a physical address. (further reading)
8. Include privacy policy and about page – These are key pages which help with trust from both users and search engines. (further reading)
9. Minimise boiler plate text – Keep duplicated text in layouts (i.e. sidebars) to a minimum. (further reading)
10. If you are targeting local SEO include your address in layout – Add your physical address and contact details to your page layout when targeting local keywords . (further reading)
11. Use www. or non www – Whichever you choose, ensure your site is only accessible and indexable by either www or non www. Best practice is to also set the preferred domain in webmaster tools. (further reading)
Part 2: Keyword Research
12. Choose your keywords wisely – Keyword research continues to be an important part of SEO. Use Google keyword planner, or advanced tools such asLong Tail Pro, to evaluate search volumes and select keywords that you wish to rank for. (further reading)
13. Select one main keyword per page – Each page on your site should targetone keyword. Avoid keyword cannibalisation (i.e. targeting the same keyword on multiple pages). (further reading)
14. Consider user intent – While a keyword may have good volume, consider the intent behind the search and whether someone searching for that phrase is likely to be interested in your product/service. (further reading)
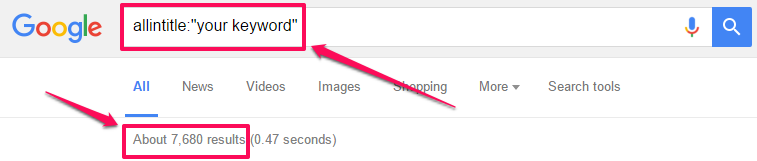
15. Check title competition – Perform a Google search for allintitle:”your keyword” to discover the number of web pages which currently contain your target keyword in the title.
16. Consider how ‘rankable’ the keyword is and how visible organic results are – There are a number of factors to consider here:
• How powerful is the competition – i.e. authority sites like Amazon, Forbes etc?
• How many links are pointing to the top sites?
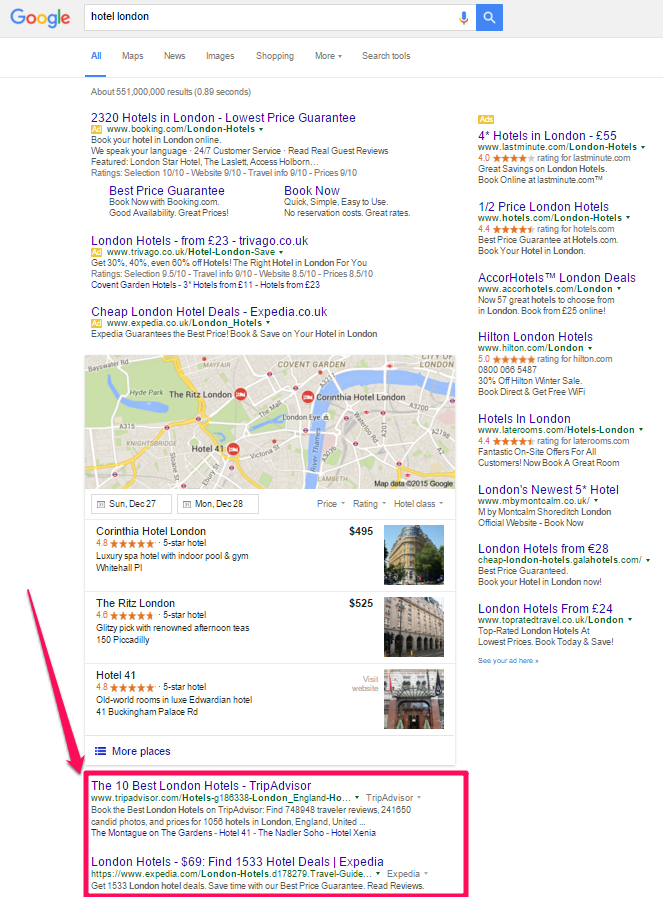
• Are organic results pushed below the fold by knowledge graph, news, ads etc (see below)?
17. Steal your competitor’s keywords – Find out exactly which keywords are driving search traffic to your competitors using Ahrefs Positions Explorer.
18. Track your rankings – Monitor progress of your website’s rankings in the search results for your target keywords. With Ahrefs Rank Tracker you can view historic data to keep track of progress of over time.
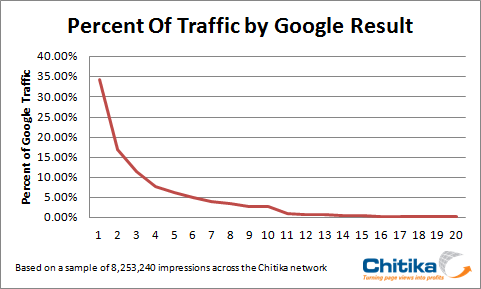
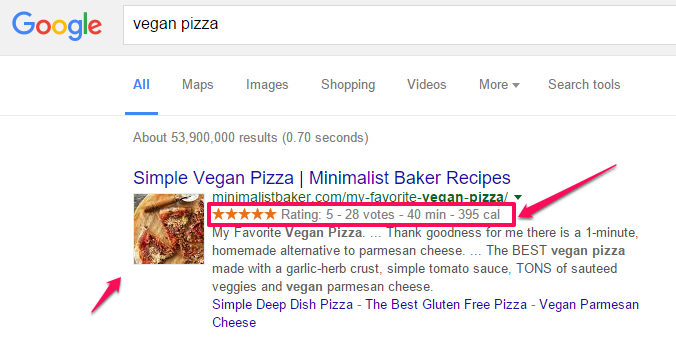
19. Monitor your click-through rate – If your web page is ranking for a target keyword you should expect to see a click-through rate (CTR) similar to the following:
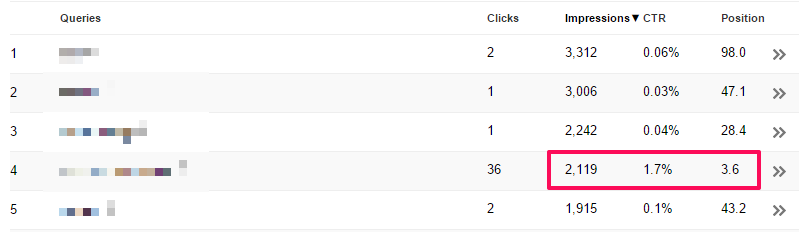
You can use the Search Analytics report in Google Webmaster Tools to check impressions and CTRs across a range of queries. In the example below, a keyword ranking at average position 3.6 is receiving a CTR of 1.7%, which is considerably below what we would expect to see for the position (should be around 7%).
In this case it may be worth split testing the page’s meta description (more on this below) to see if we can improve CTR and benefit from extra traffic.
Part 3: Title Tags
<title>This is a title tag</title>
20. Front load your keyword – Try and include your target keyword as close to the start of the title tag as possible. (further reading)
21. Avoid truncation – Title tags have 512px to play with in desktop search results, after which they will truncate. A good rule of thumb is to keep the length of your title tags to 55 characters or less, which will generally fit into this area, however, in rare cases, capitalisation and search query may still result in truncation. (further reading)
22. Make it clickable – Headlines sell newspapers and page titles ‘sell’ web pages. (further reading)
23. Stand out – If all the page titles in your niche follow a certain format, then doing something different can make your titles stand out in the SERPs. (further reading)
24. Don’t bother adding your brand – Including your brand name at the end of page titles is unnecessary – Google will often add it automatically anyway – and takes up valuable real estate. However:
25. Optimise home page for brand – The exception to this is your home page, where your title should generally be optimised for your brand.
26. Minimise stop words – With limited space to play with try and minimise use of stop/joining words – “a, and, is, on, of, or, the, was, with” – in page titles. (further reading)
27. Don’t repeat yourself. Don’t repeat yourself. Don’t repeat yourself. – Annoying isn’t it? Use your keyword once in the title and don’t repeat it.
Part 4: Meta Descriptions
<meta name="description" content="This is a meta description. It can help your content stand out in search results and improve CTR" />
28. Sell your content – Your meta description is like your advert in the search results. Write a unique, compelling meta description for each page on your site, that communicates USPs/value, and entices click-throughs. (further reading)
29. Avoid truncation – Keep your meta descriptions to around 155 characters(maximum) to minimise truncation in the search results. (further reading)
30. Use your keyword in the meta description – While not having a direct influence on ranking, keywords in meta descriptions will be bolded in search results which can help to improve CTR.
31. Split test – Experiment with different meta description formats to optimise CTR. (further reading)
Part 5: Header Tags
32. Ensure each page has a unique H1 tag – Every page on your site should have a unique H1 tag.
33. Use your keyword in the H1 Tag – The H1 tag continues to be an important on-page ranking factor and should include the page’s target keyword. (further reading)
34. Include secondary and LSI keywords – Additional header tags (H2, H3) are a good opportunity to target secondary key phrases and LSI (latent semantic indexing) keywords. (further reading)
35. Avoid using header tags in layout – Many templates use header tags in their layout with generic words/phrases such as ‘More Details’. These should be replaced with CSS styled divs.
Part 6: The Content
36. Use your keyword early – Where possible (without being forced), use your target keyword in the first paragraph of your page’s content to reinforce the topic.
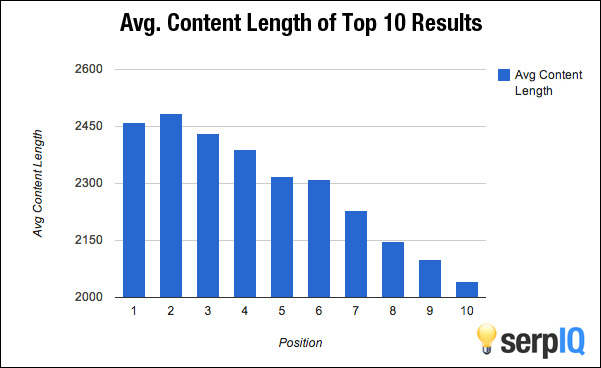
37. Long content correlates with higher rankings – Numerous studies have concluded that there is a correlation between long form content and higher rankings, although the caveat should be that this may have more to do with quality than actual length. Either way, the takeaway is to go in-depth and createthe authority page for your target keyword. (further reading and image)
38. Forget keyword density – Don’t sweat keyword density. Write naturally and you will tend to use your target keyword several times within your content without having to think about it. Just make sure to include it at least once!(further reading)
39. Use LSI keywords – LSI keywords are words that are semantically related to your main keyword. They are useful for cementing a page’s topic and also for differentiating homonyms (same words with different meaning, i.e. “bark” the sound a dog makes, “bark” the outer layer of a tree) in search queries. When writing about a topic you will tend to use these naturally, but it can be an idea to do some research beforehand. (further reading)
40. Add multimedia – Adding multimedia to your content – images, videos , slideshows etc – makes it more engaging, shareable and linkable. There may also be some direct SEO benefit. (further reading)
41. Add internal links – Adding internal links to other pages from within content allows link equity to flow round your site and also encourages reader exploration, lowering bounce rate. An often criminally under-utilised aspect of SEO. (further reading)
42. Link out – Linking out to high quality, authoritative, and topically related content aids relevance and builds relationships with other site owners in your niche. Best practice is to open external links in a new tab/window. (further reading)
43. Keep content up to date – Regularly update old/archive content to keep it fresh, relevant and rankworthy. (further reading)
44. Prioritise quality over frequency – With the exception of large publications, and news sites (which require lots of daily content), most sites will get more benefit by focusing on content quality, as opposed to frequency. Publishing 1 great article a week is better than publishing 1 mediocre article daily. (further reading)\
45. Set up rich snippets/structured data – Set up and test structured data to benefit from rich snippets in search results. (further reading)
46. Include table of contents for long content – Include a table of contents with internal links to specific sections on long pages to benefit from wikipedia style ‘jump to’ links (below) in the search results. (further reading)
Part 7: Trimming The Fat
47. Set canonical URLs – Add the canonical link element to set preferred URL for pages with similar content.
<link rel="canonical" href="http://example.com/the-defacto-version-of-the-page/">
For example, eCommerce systems which allow filtering of categories by various attributes may automatically create multiple URLs with very similar content.(further reading)
48. Add noindex, follow to pages you wish to exclude from Google – Exclude thin/worthless pages from Google’s index by adding the robots meta tag with “content” set to “noindex, follow”.
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow">
Examples of pages you may want to exclude, include tag and author archives in WordPress, however, use this tag with caution. (further reading)
49. Block spiders from sensitive content with robots.txt – Exclude Googlebot and other crawlers from sensitive parts of your site (such as admin) by blocking them in robots.txt. (further reading)
Part 8: User Experience
50. Lower your bounce rate – For most sites (save for certain affiliate sites where you want the visitor in and out) a low bounce rate and a high number of pages per session is desirable.
While it is up for debate whether Google uses the bounce rate you see in Analytics as a ranking factor (I would say they don’t), what is almost certain is that they do use and measure ‘bounce’ time back to search results, and also whether a searcher then goes on to click other results. A reasonably fast bounce from your page, followed by a click onto another result, is a strong signal that your page either did not satisfy the user’s search query, or gave a poor user experience. (further reading)
51. Use scroll map – Scroll map software will show you how far down an individual page users are scrolling, helping you determine why they may be abandoning a page before reading to the end. (further reading)
52. Use heat map tracking – Find out exactly where your visitors are clicking and interacting with your pages to optimise conversions and place navigational elements. (further reading)
53. Minimise pop-ups – While popups can be good for conversions, too many of them can send a visitor straight to the back button.
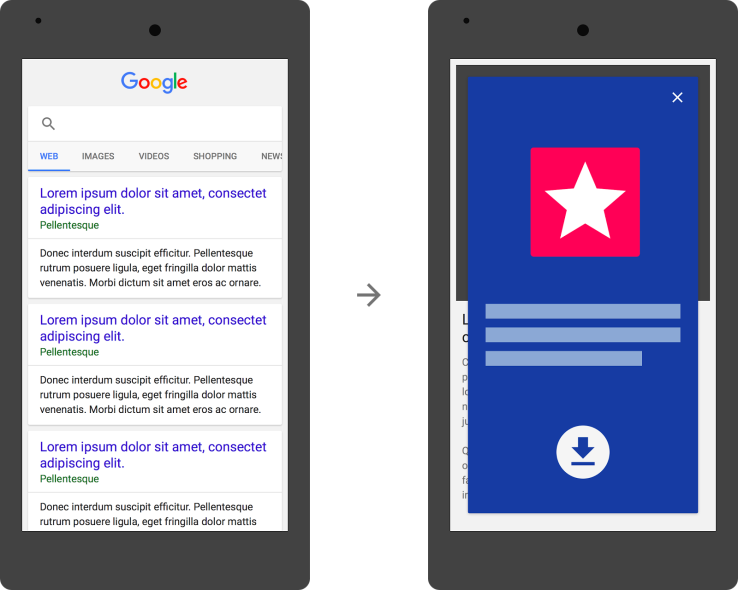
54. Be careful with interstitial ads – Google has confirmed it may choose to penalise sites that display interstitial, full screen ads (below) to users on mobile devices. (further reading)
54. Be careful with interstitial ads – Google has confirmed it may choose to penalise sites that display interstitial, full screen ads (below) to users on mobile devices.
55. Ensure website is mobile optimised – If your website is not mobile optimised you are/will be missing out on a huge amount of traffic. Make it priority #1. (further reading)
56. Consider accessibility – Your website should be functional across a wide range of devices, operating systems, screen sizes, and should be accessible to users with a disability. (further reading)
57. Consider readability – Make sure text content is easy to read and well formatted. Proof read your copy for spelling/grammatical errors. (further reading)
58. Set up friendly 404 page – Create a user friendly 404 (not found error) page, which directs visitors to relevant content and minimises bounce. (further reading)
59. Minimise down time – Ensure you have a reliable web host with minimal(ideally ZERO) down time. Don’t skimp on hosting.
60. Implement SSL – Moving your entire website to SSL should be considered(Google gives a small rankings boost to sites accessible over HTTPS), however, at a minimum, any pages which capture user information should be safely encrypted. (further reading)
Part 9: Google Webmaster Tools (Search Console)
61. Look for ‘quick wins’ – Use the search analytics report, ordered by impressions, to look for keywords with a high number of impressions and average search position 11+. Adding some internal links to these pages, or even just making sure that the exact phrase is included on the page, can be enough to move the keyword into the top 10 and instantly boost traffic.
62. Check for errors – Regularly check for (and fix) errors in the ‘Crawl Errors’ report.
63. Submit a site map/site maps – You may want to add a sitemap, or sitemaps to ensure all pages on your site can be found, and to set crawl priority. (further reading)
Part 10: Google Analytics
64. Sign up for Google Analytics – Accurate traffic stats are essential to monitor the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
65. Regularly check stats and react to any changes in traffic – Check your stats regularly to look for changes in traffic, landing pages etc and react accordingly.
Part 11: Site Speed
66. Optimise your load speed – Page load speed is a ranking factor and, all else being equal, a faster loading page will outrank a slower loading page. (further reading)
67. Test your site’s load speed – Use a tool such as Pingdom to test your site’s loading speed.
68. Implement recommendations from Google Page Speed Insights – Run your website through Google’s Page Speed Insights tool and implement recommended changes where practical.
Recommended: Check out this excellent Page Speed test and resource from Varvy.com
Part 12: Image Optimisation
69. Use them! – Include images in your content to make it more visually interesting and shareable. High quality, custom images also make for excellent link bait. (further reading)
70. Add relevant alt text – Add relevant alt text to your images. (further reading)
71. Use descriptive file names – Use descriptive file names. (further reading)
Good: <img src="photo-of-a-clown.jpg" alt="photo of a clown" />
Bad: <img src="1550111.jpg" alt"" />
72. Optimise file size – Compress images to reduce load time.
Part 13: Link Building
73. Build them! – Inbound links continue to be one of the primary factors Google uses to rank web pages.
74. Links from authoritiative domains pass more power – The more trust and authority a domain has, the more beneficial a link from it is likely to be to your rankings. You can use the Domain Rating figure (DR) in Ahrefs Site Explorer to quickly assess the relative strength of a domain (high DR = high authority). Other metrics to consider include DA (Moz) and Trust Flow (Majestic).
75. Links from topically related sites assist rankings – Links from quality sites within your niche, or pages which are topically related to your content are beneficial for rankings. (further reading)
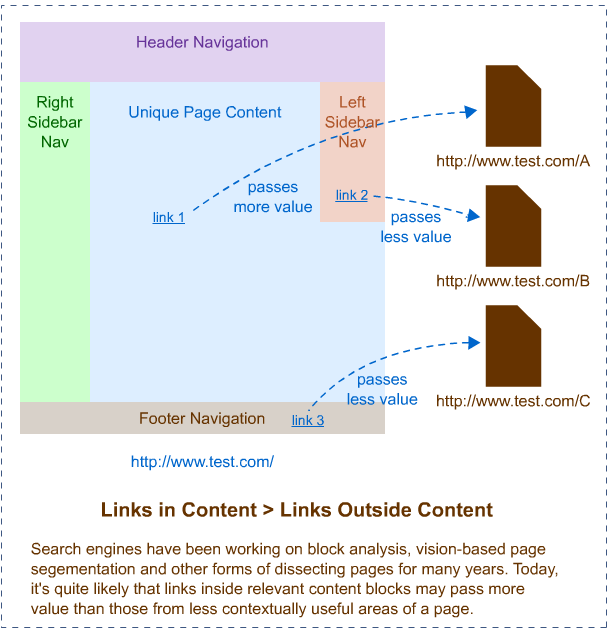
76. Links from within content are the most valuable – Editorial links from within content are considered to be the strongest links. (further reading and image)
77. Steal your competitor’s links – An analysis of your competitor’s backlink profile is a great starting point for any link building campaign. Use Ahrefs Site Explorer to easily uncover your competitor’s links and go ahead and grab them for your own site. (further reading)
78. Low quality link building may cause penalties – Low quality and automated link building may cause your site to be penalised by Google. (further reading)
79. Diversify your link profile – A strong link profile should include several different types of link. (further reading)
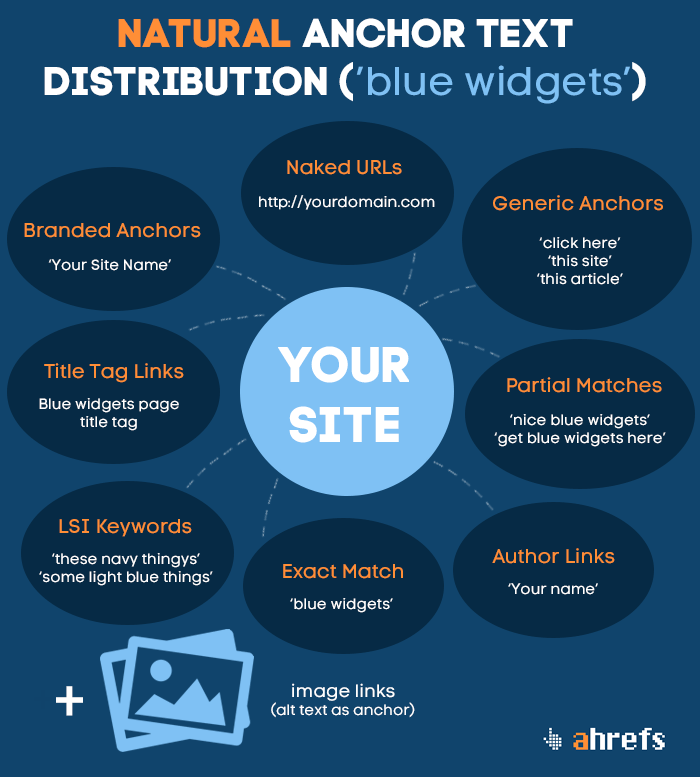
80. Diversify your anchor text – Keyword usage is anchor text is still a ranking factor, however, it is important to diversify it. A mixture of branded, generic, and keyword based anchors is desirable. (further reading)
81. Regularly audit your link profile – Conduct a regular audit of your link profile and look out for suspicious/unnatural looking links. While a small number should not do you any harm, large quantities of low quality links may be an indication of low quality link building by an SEO company, or even a negative SEO campaign from a competitor. If this is the case then you should consider removing or disavowing these links. (further reading)
Part 14: Social Media
82. Don’t ignore social media! – While officially not having a direct influence on rankings (although opinions vary on this), social media helps to spread your content and get it in front of potentially linking eyeballs. Additionally traffic from social may cause other factors that do directly influence rankings (i.e. traffic, buzz, brand searches, typed in URL searches). (further reading)
83. Use social media to share you content – Maintain active social media profiles on the major networks and share your content with your audience.
84. Show social proof – Displaying social share counts (although sadly Twitter’s is no more) acts as social proof and can lead to further shares.
85. Encourage sharing of your content – Display social share buttons in prominent positions on your web pages to make sharing as easy as possible.(further reading)
86. Include open graph data – Ensure your web pages are set up with open graph meta data for rich Facebook shares. (further reading)
87. Set up Twitter card – Enables enhanced tweets. (further reading)
88. Set up rich pins – Enabling rich pins on your website can lead to increased traffic from Pinterest. (further reading)
Part 15: Google Penalty Recovery
89. Manual penalties – Manual webspam penalties will generally be notified by email and a message in webmaster tools. (further reading)
90. Check traffic drops against Google update dates – Drops in traffic that align with Google updates are an early indication of algorithmic penalties.(further reading)
91. Remove/minimise thin content – For penalties which align with Panda updates identify pages with thin/duplicate content and either remove, ‘beef up’ or de-index. (further reading)
92. Remove bad links – Conduct a link audit, flag all low quality links and reach out to linking sites requesting removal. (further reading)
93. Disavow any links which cannot be removed – If no response to removal requests add low quality links/domains to a disavow file. You can manage multiple disavow files from within Ahrefs. (further reading)
94. Check for hacks/inserted links – Ensure your website has not been hacked and that there are no suspicious outgoing links. (further reading)
95. File reconsideration request – For manual penalties, you should file a reconsideration request once all identifiable issues have been resolved. (further reading)
Note: Recovery from penalties is not straight forward and you should be very careful when removing links, de-indexing pages etc. If in doubt consider employing the services of an experienced SEO consultant. It should also be noted that Google is expected to transition to ‘real-time’, continuous Penguin/Panda updates in the near future, which may make identifying specific penalties harder.
Part 16: Content Promotion
96. Find popular content in your niche and improve/update it – Take the guesswork out of content creation by finding previously popular content and making it even better. The great thing about this strategy is that you can reach out to those who linked to/shared the original content and point them to your own content. (further reading)
Here’s Tim showing how to use Ahrefs Content Explorer to easily find popular content in your niche and pull a report of all linking sites.
97. Spend at least as must time promoting content as creating it – Unless you already have a huge following, the ‘build it and they will come’ approach to marketing content just doesn’t cut it. You should spend at least as much time promoting your content as you do creating it, and indeed some content marketing experts, such as Derek Halpern of Social Triggers, argue that content promotion should take up the lion’s share of your time. (further reading)
98. Email outreach continues to be most powerful method – The best way to get your content in front of someone is to send them an email (but see tip number 108).
99. Shareable assets = more links – Include high quality shareable assets such as infographics in your content to increase social shares and links.
100. Share content from others – You scratch my back, I’ll scratch yours. Leverage the power of the law of reciprocity.
Part 17: SEO Housekeeping
101. Fix broken links – Broken links are bad for user experience and bad for SEO. Find them and fix them.
102. Moderate comments/UGC – Be sure to carefully moderate any user generated content (i.e. blog comments, forums etc) to check for spam and links to low quality sites/bad neighborhoods.
Part 18: General SEO Tips & Advice
103. Don’t put your eggs in one basket – A good internet marketing campaign should be multi-faceted and include a mix of SEO, social media, and paid traffic. Never rely on one source of traffic for your business. (further reading)
104. Learn as much as you can – Knowledge is power. There are a load of greatSEO blogs offering free advice, so learn as much as you can. Subscribing to Ahrefs blog below would be a good start
105. Pay attention to updates – Things change in SEO, so keep up to date with those changes.
Referral - www.ahrefs.com
Then look no further.
We’ve created a list of over 100 SEO tips and best pratices and split them into logical sections to cover various aspects of search engine optimisation – from on-page factors, to user experience, link building and more.
For most tips you will also find a link to further reading; including official Google guidelines where relevant and a hand picked selection of some of the very best SEO guides on the web.
To jump to a specific section, use the quick links on the right, otherwise, let’s get started!
Part 1: Site Layout & Architecture
1. Ensure content is clear and upfront – Content should be front and centre on any web page. At a minimum the page’s title should be ‘above the fold’; that is visible without the visitor having to scroll. (further reading)
2. Avoid too many ads above the fold – While display advertising is an essential revenue model for many websites, too many ads above the fold may impact negatively on search rankings. Ensure any display advertising is non intrusive and clearly distinguishable from content. (further reading)
3. Create a content hierarchy – A well designed hierarchy keeps content organised and allows pagerank to flow effectively round a website, boosting key ‘hub’ pages.
4. Ensure navigation is clear – Navigation should be easy to locate and intuitive for both search engines and users. (further reading)
5. Nofollow any paid/affiliate links – All paid links should have the rel=”nofollow” attribute added. This includes affiliate links. (further reading)
<a href="http://www.example.com" rel="nofollow">Paid Link</a>
6. Use SEO friendly URLs – URLs should be human readable and follow a logical structure. Short URLs which include target keywords (separated by hyphens) are considered best for SEO. (further reading)
7. Ensure you have clearly visible contact information – Contact details should be easy to find and ideally should include a physical address. (further reading)
8. Include privacy policy and about page – These are key pages which help with trust from both users and search engines. (further reading)
9. Minimise boiler plate text – Keep duplicated text in layouts (i.e. sidebars) to a minimum. (further reading)
10. If you are targeting local SEO include your address in layout – Add your physical address and contact details to your page layout when targeting local keywords . (further reading)
11. Use www. or non www – Whichever you choose, ensure your site is only accessible and indexable by either www or non www. Best practice is to also set the preferred domain in webmaster tools. (further reading)
Part 2: Keyword Research
12. Choose your keywords wisely – Keyword research continues to be an important part of SEO. Use Google keyword planner, or advanced tools such asLong Tail Pro, to evaluate search volumes and select keywords that you wish to rank for. (further reading)
13. Select one main keyword per page – Each page on your site should targetone keyword. Avoid keyword cannibalisation (i.e. targeting the same keyword on multiple pages). (further reading)
14. Consider user intent – While a keyword may have good volume, consider the intent behind the search and whether someone searching for that phrase is likely to be interested in your product/service. (further reading)
15. Check title competition – Perform a Google search for allintitle:”your keyword” to discover the number of web pages which currently contain your target keyword in the title.
16. Consider how ‘rankable’ the keyword is and how visible organic results are – There are a number of factors to consider here:
• How powerful is the competition – i.e. authority sites like Amazon, Forbes etc?
• How many links are pointing to the top sites?
• Are organic results pushed below the fold by knowledge graph, news, ads etc (see below)?
17. Steal your competitor’s keywords – Find out exactly which keywords are driving search traffic to your competitors using Ahrefs Positions Explorer.
18. Track your rankings – Monitor progress of your website’s rankings in the search results for your target keywords. With Ahrefs Rank Tracker you can view historic data to keep track of progress of over time.
19. Monitor your click-through rate – If your web page is ranking for a target keyword you should expect to see a click-through rate (CTR) similar to the following:
You can use the Search Analytics report in Google Webmaster Tools to check impressions and CTRs across a range of queries. In the example below, a keyword ranking at average position 3.6 is receiving a CTR of 1.7%, which is considerably below what we would expect to see for the position (should be around 7%).
In this case it may be worth split testing the page’s meta description (more on this below) to see if we can improve CTR and benefit from extra traffic.
Part 3: Title Tags
<title>This is a title tag</title>
20. Front load your keyword – Try and include your target keyword as close to the start of the title tag as possible. (further reading)
21. Avoid truncation – Title tags have 512px to play with in desktop search results, after which they will truncate. A good rule of thumb is to keep the length of your title tags to 55 characters or less, which will generally fit into this area, however, in rare cases, capitalisation and search query may still result in truncation. (further reading)
22. Make it clickable – Headlines sell newspapers and page titles ‘sell’ web pages. (further reading)
23. Stand out – If all the page titles in your niche follow a certain format, then doing something different can make your titles stand out in the SERPs. (further reading)
24. Don’t bother adding your brand – Including your brand name at the end of page titles is unnecessary – Google will often add it automatically anyway – and takes up valuable real estate. However:
25. Optimise home page for brand – The exception to this is your home page, where your title should generally be optimised for your brand.
26. Minimise stop words – With limited space to play with try and minimise use of stop/joining words – “a, and, is, on, of, or, the, was, with” – in page titles. (further reading)
27. Don’t repeat yourself. Don’t repeat yourself. Don’t repeat yourself. – Annoying isn’t it? Use your keyword once in the title and don’t repeat it.
Part 4: Meta Descriptions
<meta name="description" content="This is a meta description. It can help your content stand out in search results and improve CTR" />
28. Sell your content – Your meta description is like your advert in the search results. Write a unique, compelling meta description for each page on your site, that communicates USPs/value, and entices click-throughs. (further reading)
29. Avoid truncation – Keep your meta descriptions to around 155 characters(maximum) to minimise truncation in the search results. (further reading)
30. Use your keyword in the meta description – While not having a direct influence on ranking, keywords in meta descriptions will be bolded in search results which can help to improve CTR.
31. Split test – Experiment with different meta description formats to optimise CTR. (further reading)
Part 5: Header Tags
32. Ensure each page has a unique H1 tag – Every page on your site should have a unique H1 tag.
33. Use your keyword in the H1 Tag – The H1 tag continues to be an important on-page ranking factor and should include the page’s target keyword. (further reading)
34. Include secondary and LSI keywords – Additional header tags (H2, H3) are a good opportunity to target secondary key phrases and LSI (latent semantic indexing) keywords. (further reading)
35. Avoid using header tags in layout – Many templates use header tags in their layout with generic words/phrases such as ‘More Details’. These should be replaced with CSS styled divs.
Part 6: The Content
36. Use your keyword early – Where possible (without being forced), use your target keyword in the first paragraph of your page’s content to reinforce the topic.
37. Long content correlates with higher rankings – Numerous studies have concluded that there is a correlation between long form content and higher rankings, although the caveat should be that this may have more to do with quality than actual length. Either way, the takeaway is to go in-depth and createthe authority page for your target keyword. (further reading and image)
38. Forget keyword density – Don’t sweat keyword density. Write naturally and you will tend to use your target keyword several times within your content without having to think about it. Just make sure to include it at least once!(further reading)
39. Use LSI keywords – LSI keywords are words that are semantically related to your main keyword. They are useful for cementing a page’s topic and also for differentiating homonyms (same words with different meaning, i.e. “bark” the sound a dog makes, “bark” the outer layer of a tree) in search queries. When writing about a topic you will tend to use these naturally, but it can be an idea to do some research beforehand. (further reading)
40. Add multimedia – Adding multimedia to your content – images, videos , slideshows etc – makes it more engaging, shareable and linkable. There may also be some direct SEO benefit. (further reading)
41. Add internal links – Adding internal links to other pages from within content allows link equity to flow round your site and also encourages reader exploration, lowering bounce rate. An often criminally under-utilised aspect of SEO. (further reading)
42. Link out – Linking out to high quality, authoritative, and topically related content aids relevance and builds relationships with other site owners in your niche. Best practice is to open external links in a new tab/window. (further reading)
43. Keep content up to date – Regularly update old/archive content to keep it fresh, relevant and rankworthy. (further reading)
44. Prioritise quality over frequency – With the exception of large publications, and news sites (which require lots of daily content), most sites will get more benefit by focusing on content quality, as opposed to frequency. Publishing 1 great article a week is better than publishing 1 mediocre article daily. (further reading)\
45. Set up rich snippets/structured data – Set up and test structured data to benefit from rich snippets in search results. (further reading)
46. Include table of contents for long content – Include a table of contents with internal links to specific sections on long pages to benefit from wikipedia style ‘jump to’ links (below) in the search results. (further reading)
Part 7: Trimming The Fat
47. Set canonical URLs – Add the canonical link element to set preferred URL for pages with similar content.
<link rel="canonical" href="http://example.com/the-defacto-version-of-the-page/">
For example, eCommerce systems which allow filtering of categories by various attributes may automatically create multiple URLs with very similar content.(further reading)
48. Add noindex, follow to pages you wish to exclude from Google – Exclude thin/worthless pages from Google’s index by adding the robots meta tag with “content” set to “noindex, follow”.
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow">
Examples of pages you may want to exclude, include tag and author archives in WordPress, however, use this tag with caution. (further reading)
49. Block spiders from sensitive content with robots.txt – Exclude Googlebot and other crawlers from sensitive parts of your site (such as admin) by blocking them in robots.txt. (further reading)
Part 8: User Experience
50. Lower your bounce rate – For most sites (save for certain affiliate sites where you want the visitor in and out) a low bounce rate and a high number of pages per session is desirable.
While it is up for debate whether Google uses the bounce rate you see in Analytics as a ranking factor (I would say they don’t), what is almost certain is that they do use and measure ‘bounce’ time back to search results, and also whether a searcher then goes on to click other results. A reasonably fast bounce from your page, followed by a click onto another result, is a strong signal that your page either did not satisfy the user’s search query, or gave a poor user experience. (further reading)
51. Use scroll map – Scroll map software will show you how far down an individual page users are scrolling, helping you determine why they may be abandoning a page before reading to the end. (further reading)
52. Use heat map tracking – Find out exactly where your visitors are clicking and interacting with your pages to optimise conversions and place navigational elements. (further reading)
53. Minimise pop-ups – While popups can be good for conversions, too many of them can send a visitor straight to the back button.
54. Be careful with interstitial ads – Google has confirmed it may choose to penalise sites that display interstitial, full screen ads (below) to users on mobile devices. (further reading)
54. Be careful with interstitial ads – Google has confirmed it may choose to penalise sites that display interstitial, full screen ads (below) to users on mobile devices.
55. Ensure website is mobile optimised – If your website is not mobile optimised you are/will be missing out on a huge amount of traffic. Make it priority #1. (further reading)
56. Consider accessibility – Your website should be functional across a wide range of devices, operating systems, screen sizes, and should be accessible to users with a disability. (further reading)
57. Consider readability – Make sure text content is easy to read and well formatted. Proof read your copy for spelling/grammatical errors. (further reading)
58. Set up friendly 404 page – Create a user friendly 404 (not found error) page, which directs visitors to relevant content and minimises bounce. (further reading)
59. Minimise down time – Ensure you have a reliable web host with minimal(ideally ZERO) down time. Don’t skimp on hosting.
60. Implement SSL – Moving your entire website to SSL should be considered(Google gives a small rankings boost to sites accessible over HTTPS), however, at a minimum, any pages which capture user information should be safely encrypted. (further reading)
Part 9: Google Webmaster Tools (Search Console)
61. Look for ‘quick wins’ – Use the search analytics report, ordered by impressions, to look for keywords with a high number of impressions and average search position 11+. Adding some internal links to these pages, or even just making sure that the exact phrase is included on the page, can be enough to move the keyword into the top 10 and instantly boost traffic.
62. Check for errors – Regularly check for (and fix) errors in the ‘Crawl Errors’ report.
63. Submit a site map/site maps – You may want to add a sitemap, or sitemaps to ensure all pages on your site can be found, and to set crawl priority. (further reading)
Part 10: Google Analytics
64. Sign up for Google Analytics – Accurate traffic stats are essential to monitor the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
65. Regularly check stats and react to any changes in traffic – Check your stats regularly to look for changes in traffic, landing pages etc and react accordingly.
Part 11: Site Speed
66. Optimise your load speed – Page load speed is a ranking factor and, all else being equal, a faster loading page will outrank a slower loading page. (further reading)
67. Test your site’s load speed – Use a tool such as Pingdom to test your site’s loading speed.
68. Implement recommendations from Google Page Speed Insights – Run your website through Google’s Page Speed Insights tool and implement recommended changes where practical.
Recommended: Check out this excellent Page Speed test and resource from Varvy.com
Part 12: Image Optimisation
69. Use them! – Include images in your content to make it more visually interesting and shareable. High quality, custom images also make for excellent link bait. (further reading)
70. Add relevant alt text – Add relevant alt text to your images. (further reading)
71. Use descriptive file names – Use descriptive file names. (further reading)
Good: <img src="photo-of-a-clown.jpg" alt="photo of a clown" />
Bad: <img src="1550111.jpg" alt"" />
72. Optimise file size – Compress images to reduce load time.
Part 13: Link Building
73. Build them! – Inbound links continue to be one of the primary factors Google uses to rank web pages.
74. Links from authoritiative domains pass more power – The more trust and authority a domain has, the more beneficial a link from it is likely to be to your rankings. You can use the Domain Rating figure (DR) in Ahrefs Site Explorer to quickly assess the relative strength of a domain (high DR = high authority). Other metrics to consider include DA (Moz) and Trust Flow (Majestic).
75. Links from topically related sites assist rankings – Links from quality sites within your niche, or pages which are topically related to your content are beneficial for rankings. (further reading)
76. Links from within content are the most valuable – Editorial links from within content are considered to be the strongest links. (further reading and image)
77. Steal your competitor’s links – An analysis of your competitor’s backlink profile is a great starting point for any link building campaign. Use Ahrefs Site Explorer to easily uncover your competitor’s links and go ahead and grab them for your own site. (further reading)
78. Low quality link building may cause penalties – Low quality and automated link building may cause your site to be penalised by Google. (further reading)
79. Diversify your link profile – A strong link profile should include several different types of link. (further reading)
80. Diversify your anchor text – Keyword usage is anchor text is still a ranking factor, however, it is important to diversify it. A mixture of branded, generic, and keyword based anchors is desirable. (further reading)
81. Regularly audit your link profile – Conduct a regular audit of your link profile and look out for suspicious/unnatural looking links. While a small number should not do you any harm, large quantities of low quality links may be an indication of low quality link building by an SEO company, or even a negative SEO campaign from a competitor. If this is the case then you should consider removing or disavowing these links. (further reading)
Part 14: Social Media
82. Don’t ignore social media! – While officially not having a direct influence on rankings (although opinions vary on this), social media helps to spread your content and get it in front of potentially linking eyeballs. Additionally traffic from social may cause other factors that do directly influence rankings (i.e. traffic, buzz, brand searches, typed in URL searches). (further reading)
83. Use social media to share you content – Maintain active social media profiles on the major networks and share your content with your audience.
84. Show social proof – Displaying social share counts (although sadly Twitter’s is no more) acts as social proof and can lead to further shares.
85. Encourage sharing of your content – Display social share buttons in prominent positions on your web pages to make sharing as easy as possible.(further reading)
86. Include open graph data – Ensure your web pages are set up with open graph meta data for rich Facebook shares. (further reading)
87. Set up Twitter card – Enables enhanced tweets. (further reading)
88. Set up rich pins – Enabling rich pins on your website can lead to increased traffic from Pinterest. (further reading)
Part 15: Google Penalty Recovery
89. Manual penalties – Manual webspam penalties will generally be notified by email and a message in webmaster tools. (further reading)
90. Check traffic drops against Google update dates – Drops in traffic that align with Google updates are an early indication of algorithmic penalties.(further reading)
91. Remove/minimise thin content – For penalties which align with Panda updates identify pages with thin/duplicate content and either remove, ‘beef up’ or de-index. (further reading)
92. Remove bad links – Conduct a link audit, flag all low quality links and reach out to linking sites requesting removal. (further reading)
93. Disavow any links which cannot be removed – If no response to removal requests add low quality links/domains to a disavow file. You can manage multiple disavow files from within Ahrefs. (further reading)
94. Check for hacks/inserted links – Ensure your website has not been hacked and that there are no suspicious outgoing links. (further reading)
95. File reconsideration request – For manual penalties, you should file a reconsideration request once all identifiable issues have been resolved. (further reading)
Note: Recovery from penalties is not straight forward and you should be very careful when removing links, de-indexing pages etc. If in doubt consider employing the services of an experienced SEO consultant. It should also be noted that Google is expected to transition to ‘real-time’, continuous Penguin/Panda updates in the near future, which may make identifying specific penalties harder.
Part 16: Content Promotion
96. Find popular content in your niche and improve/update it – Take the guesswork out of content creation by finding previously popular content and making it even better. The great thing about this strategy is that you can reach out to those who linked to/shared the original content and point them to your own content. (further reading)
Here’s Tim showing how to use Ahrefs Content Explorer to easily find popular content in your niche and pull a report of all linking sites.
97. Spend at least as must time promoting content as creating it – Unless you already have a huge following, the ‘build it and they will come’ approach to marketing content just doesn’t cut it. You should spend at least as much time promoting your content as you do creating it, and indeed some content marketing experts, such as Derek Halpern of Social Triggers, argue that content promotion should take up the lion’s share of your time. (further reading)
98. Email outreach continues to be most powerful method – The best way to get your content in front of someone is to send them an email (but see tip number 108).
99. Shareable assets = more links – Include high quality shareable assets such as infographics in your content to increase social shares and links.
100. Share content from others – You scratch my back, I’ll scratch yours. Leverage the power of the law of reciprocity.
Part 17: SEO Housekeeping
101. Fix broken links – Broken links are bad for user experience and bad for SEO. Find them and fix them.
102. Moderate comments/UGC – Be sure to carefully moderate any user generated content (i.e. blog comments, forums etc) to check for spam and links to low quality sites/bad neighborhoods.
Part 18: General SEO Tips & Advice
103. Don’t put your eggs in one basket – A good internet marketing campaign should be multi-faceted and include a mix of SEO, social media, and paid traffic. Never rely on one source of traffic for your business. (further reading)
104. Learn as much as you can – Knowledge is power. There are a load of greatSEO blogs offering free advice, so learn as much as you can. Subscribing to Ahrefs blog below would be a good start
105. Pay attention to updates – Things change in SEO, so keep up to date with those changes.
Referral - www.ahrefs.com

















9 comments:
Thanks for Sharing the Informative Article on Divorce Procedure and Divorce Certificate
Thanks for sharing useful information. Please also write about Scrap for sale, Scrap buyer and Onshore and Offshore in UAE.
Thanks for sharing useful information. We would also like to read about Single Status Certificate in Pakistan .
Facilitate your legal union with the convenience of Online Marriage, streamlining the process for couples. Navigate the dissolution of marriage with the Khula Procedure in Pakistan, ensuring a legal and considerate approach to marital separation. These streamlined processes prioritize accessibility and adherence to legal protocols.
Thanks for sharing useful information. Please also share information about how to get the SEO Services in Kuwait and SEO Company in Dubai.
Now if you want to get the Details on Copper Material for Buy in UAE & Copper scrap for buy in UAE then you need to choose us. Thanks for Sharing the Informational Content
Now if you want to get the Details on Demolition Services in UAE then you need to choose us. Thanks for Sharing the Informational Content
Discover top-quality chemicals materials for buy in UAE! Explore a diverse range of options and find the perfect solutions for your industrial needs. Promote your sourcing experience with reliable suppliers offering Alloys material for buy in UAE.
Discover top-quality Steel scrap for buy in UAE! Explore a diverse range of options and find the perfect solutions for your industrial needs. Promote your sourcing experience with reliable suppliers offering Alloy scrap for buy in UAE.
Post a Comment